About¶
Colorply is an open source python application which add new wavelength channels to a 3D cloud of points from a set of referenced images and uses images calibration from MicMac. This package comes with a GUI, to make tasks easier if you are not used to MicMac.
These models are models oriented in the same relative coordinate system. However, these models are composed of only one channel. Colorply merges any channels from any models, as long as they are in the same coordinate system.

This project alone was made in a week, in a bigger project of photogrammetry engineering. The whole project focused in testing and evaluating a multispectral camera, the Parot Sequoia. Then, a major part used this camera to generate multispectral 3D cloud of points for remote sensing purposes like vegetation classification, all in 3D. Because MicMac works only for RGB (or maximum 3-channels images), Colorply was created and handles as many channels as you want and complete an existing 3D points from multispectral images.
Instalation¶
- This package depends on :
- PyQt5
- lxml
- plyfile
- numpy
PyQt5 is only used fot the GUI of this application. As it can be a bit tricky to understand the file and directory names generated by MicMac, we decided to create an interface for it. It is not obligatory to use this interface, you can freely use and modify the python modules.
To install this package, clone this repository and from the command line in the root folder, use :
git clone https://github.com/arthurdjn/colorply
cd nets
pip install .
Or you can download it directly with pip:
pip install colorply
This will install all the dependencies and add Colorply to your python environment, usually saved in path_to_anacondalibsite-packages.
Usage¶
Colorply works hands in hands with MicMac which is an open source photogrammetric software. You can download it from GitHub, or from the main page. If you are new to MicMac, take a look a the documentation and this active forum.
How it works¶
The interface is simple, but all options are linked !
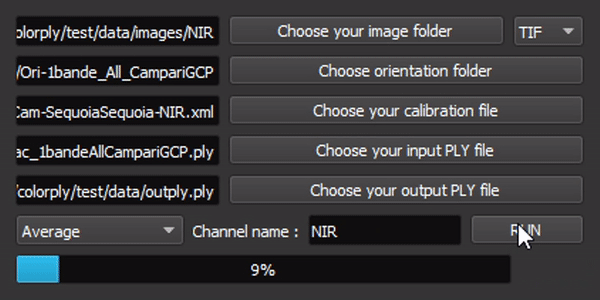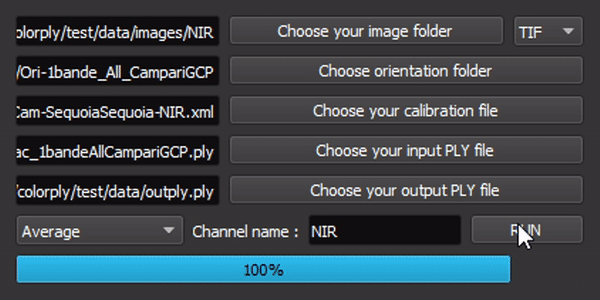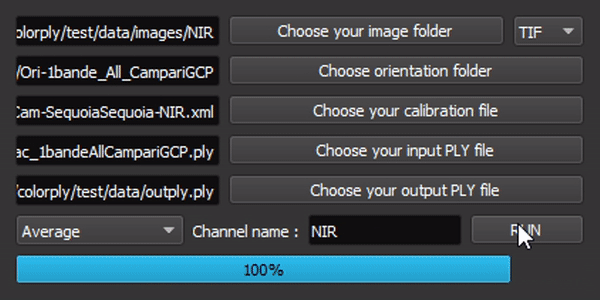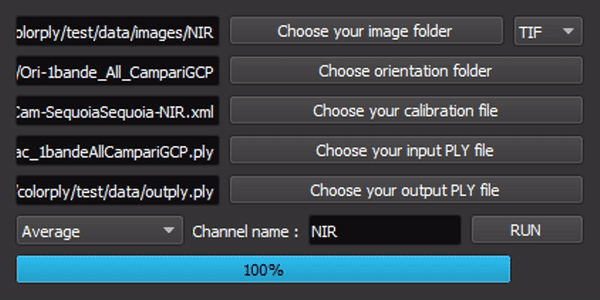
To use this package, run main.py or
from colorply.ui import interface
interface()
If you prefer doing it manually, you can use the functional implementation:
from colorply import add_cloud_channel
# Load the 3D model
input_ply = "test/data/result/RVB_GRE.ply"
# Load MicMac calibration files
calibration_file = "test/data/calibration/Ori-1bande_All_CampariGCP/AutoCal_Foc-4000_Cam-SequoiaSequoia-GRE.xml"
# Load the orientation files for all images in the scene
orientation_dir = "test/data/calibration/Ori-1bande_All_CampariGCP"
# Load the images (corresponding to the orientation files)
image_dir = "test/data/images/RED"
# Additional arguments
image_ext = "TIF"
channel = "RED"
# Resulting ply
output_ply = "output.ply"
# Project all points in `input_ply` to `images_dir`.
# Create a new ply, the operation is not inplace.
add_cloud_channel(input_ply, output_ply,
calibration_file, orientation_dir,
image_dir, image_ext, channel)
You can also use the commandlines system
python colorply --inply path/to/input_ply
--outply path/to/output_ply
--calib path/to/calib_xml
--oridir path/to/orientation_folder
--imdir path/to/image_folder
--imext image_extension
--channel name_of_new_channel
--mode mode_used_to_merge_new_radiometry
Use help –argument for additional information.